HPLC Chromatography (Questions & Answers)
HPLC is a chromatographic technique that employs a liquid mobile phase to separate and analyze components of a sample. Unlike traditional liquid chromatography, HPLC utilizes high pressure to force the liquid mobile phase through a packed column, enhancing separation efficiency and speeding up analysis times. This increased pressure allows for the use of smaller particle sizes in the stationary phase, resulting in higher resolution and sharper peaks.
Key Components of an HPLC System:
1. Mobile Phase: The liquid that carries the sample through the column is known as the mobile phase. It can be a single solvent or a mixture of solvents, depending on the nature of the compounds being analyzed.
2. Stationary Phase: The stationary phase is a packed column or a capillary tube filled with a solid support material. The choice of stationary phase depends on the type of compounds to be separated, with options ranging from reverse phase to normal phase chromatography.
3. Pump: The pump is responsible for delivering the mobile phase at a constant flow rate and high pressure, ensuring optimal separation efficiency.
4. Injector: The injector introduces the sample into the mobile phase, initiating the chromatographic process.
5. Detector: The detector monitors the eluting compounds and generates signals that are used to create chromatograms. Common detectors include UV-visible, fluorescence, and mass spectrometry detectors.
Compressed air validation in Pharmaceutical Industries
Advantages of HPLC:
1. High Sensitivity: HPLC can detect compounds at low concentrations, making it an essential technique for trace analysis.
2. High Resolution: The high pressure and small particle sizes in HPLC columns result in superior resolution of closely related compounds.
3. Versatility: HPLC can be adapted for a wide range of applications by adjusting the mobile phase, column, and detector parameters.
4. Quantitative Accuracy: The quantitative accuracy of HPLC makes it a reliable method for determining the concentration of analytes in a sample.

HPLC (Questions & answers)
Q.1- What is the difference between C8 and C18?
Answer: – C8 has 8 carbon atoms and C18 has 18 carbon atoms, C18 is more hydrophobic than C8 due to that C18 has a long retention time and C8 has a sort retention time (early).
Q.2- What is the difference between related substances and Chromatographic purity?
Answer: Related substance is used to determine known as well as unknown impurities while chromatography purity is used to determine only known impurities from the sample.
Q.3- What is the baseline in HPLC?
Answer: The baseline is a detector response to the mobile phase.
Q.4- Why buffer is used in the mobile phase?
Answer: Buffer is used resisted change in PH.
Q.5- Why guard column used in HPLC?
Answer: To protect the analytical column from contamination.
Q.6- What is the difference between a stationary phase and a mobile phase?
Answer: The stationary phase does not move with the sample it sticks in the column. While the mobile phase moves with the sample throughout the column.
Q.7- What is the carry-over in HPLC?
Answer: Void volume is a volume of mobile phase required to elute an un-retained peak.
Q.8- What is the dead volume in HPLC?
Answer: Dead volume is the volume of the HPLC system between points of injection to the point of detection.
Q.9- What is the dwell volume in HPLC?
Answer: Dwell volume is a volume of gradient HPLC system between mixing chamber in column inlet.
Q: 10- What are the most buffers used in HPLC?
Answer: Acetate buffer and phosphate buffer are the most common buffers used in HPLC.
Q.11- How should I store the HPLC column?
Answer: The normal phase column can be stored in ethanol and the reverse phase column is stored in a mixer of water and organic solvent (ANC/ Methanol).
Q.12- What is the maximum pressure in HPLC?
Answer: It depends on which make you are using for water HPLC 5000 psi.
Q.13- What is the USP general chapter number for chromatography?
Answer: USP general chapter number <621>.
Q.14- How many types of chromatography?
Answer: Two types of chromatography
- Liquid chromatography
- Gas chromatography.
Q.15- What is the full form of HPLC?
Answer: High-pressure liquid chromatography is high-performance liquid chromatography.
Q.16- Why are we called high-pressure liquid chromatography?
Answer: Because applying high pressure by using pumps to chromatography.
Q.17- What is the principle of HPLC?
Answer: HPLC is a separation technique of components from the mixer by using a solid stationary phase and a liquid mobile phase.
Q.18- What is reverse phase chromatography?
Answer: Where the mobile phase is more polar than the stationary phase is called reverse chromatography.
Q.19- What is the normal phase chromatography?
Answer: Where stationary phase is more polar than the mobile phase as called normal chromatography.
Q.20- What is the column?
Answer: A still tube that contains a stationary phase.
Q.21- What are the components of HPLC?
Answer:
- Reservoir
- Pump
- Sample component
- Column components
- Detector
- Recorder.
Q.22- What are the types of detectors used in HPLC?
Answer:
- UV detector
- PDA
- Fluorescent detector
- Conductivity detector
- Reflective detector
- Light scattering detector.
Q.23- What is the gradient run?
Answer: The mobile phase composition varies over run time
| RT | A | B |
| 1 | 30 | 70 |
| 2 | 40 | 60 |
| 3 | 50 | 50 |
| 4 | 60 | 40 |
Q.24- What is an isocratic run?
Answer: The mobile phase (mixed MP) remains the same throughout the run. Exp. from 1min to 4min, it’s the same.
Q.25- What is the linear gradient?
Answer: The mobile phase remains the same throughout the run by using two different reservoirs.
Ex.
| RT | A | B |
| 1 | 30 | 70 |
| 2 | 30 | 70 |
| 3 | 30 | 70 |
| 4 | 30 | 70 |
Q.26- What is the retention time?
Answer: It is a time between injection and the appearance peak maxima.
Q.27- What is the relative retention time?
Answer: It is a measure of the difference of affinities of two compounds for the stationary phase.
Q.28- Which standard we used for HPLC calibration?
Answer: Caffeine standard used for HPLC calibration.
Q.29- Why is the caffeine standard used for calibration?
Answer:
- It is very stable
- It is durable
- Readily available in the market.
- It shows two maxima one minimum at 205, 273, and 245 nm respectively.
Q.30- What is the most commonly used stationary phase?
Answer: Silica gel is used in the stationary phase.
Q.31- Why is silica gel used in the stationary phase?
Answer: Silica gel is an inert material and doesn’t react with the mobile phase.
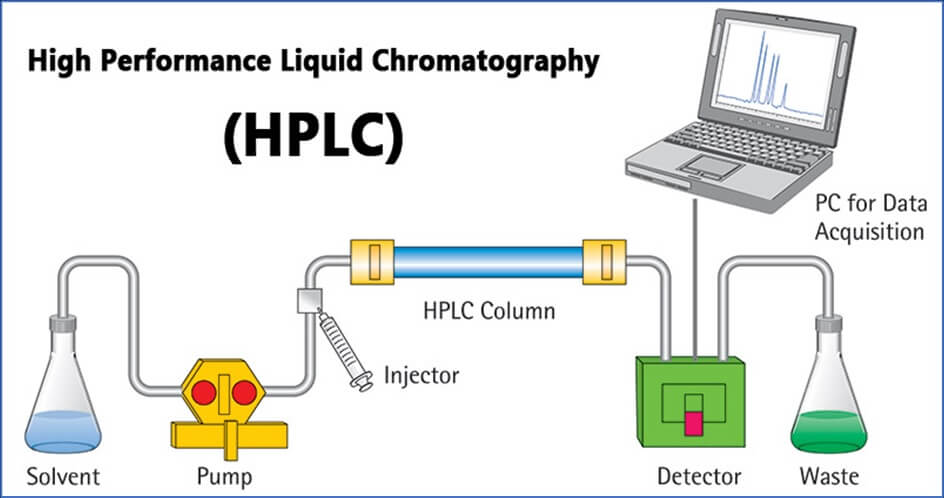
Q.32- Explain the flow diagram of the HPLC system.
Answer:
- Solvent reservoir to store MP
- Pump to move MP in pressure.
- Degasser to remove dissolved air.
- Mixing volume to mix MP
- Guard column to protect column.
- Sample injector to inert sample.
- Column to separate components.
- Detector to detect the component.
- Recorder to record the analyzed data.
- Outlet to collect waste.
