DISPENSING BOOTH
A dispensing booth is a kind of purifying equipment for materials sampling, weighing, and analysis. A dispensing booth is also called a sampling booth, a weighing booth, a downflow hood, RLAF (reverse airflow), or a powder
containment booth.
It uses the laminar airflow technique to provide dust containment and operator protection while filling, weighing,
and sampling harmful components, active ingredients, and raw powder materials.
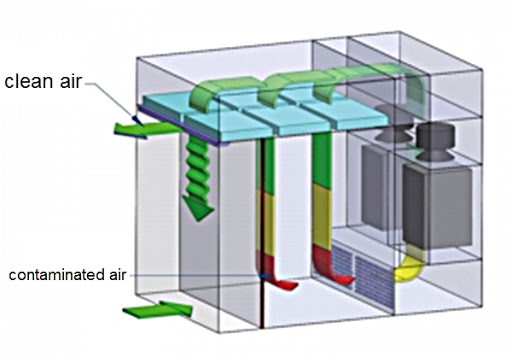
The Dispensing booth provides a unidirectional airflow (laminar airflow), in which most of the clean air enters the working zone.
Only a small amount of the air is discharged to the ambient environment, which creates negative pressure in the working zone, thereby providing a safe and clean working environment, and preventing the operators from powder contamination.
Dust, especially dust generated during the production process can be toxic. If dust is not filtered and controlled, it not only causes environmental contamination but also threatens workers’ health and safety.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the manufacture of drugs can generate hazardous dust, especially when weighing, and dispensing materials in powder form. Therefore, a dispensing booth is important. As a result, it is also called a pharmaceutical (powder) weighing booth, or pharmaceutical sampling booth.
Dispensing booth structure
The dispensing booth has a stainless steel structure with main components including pre-filter (10 microns), fine filter (3 microns), HEPA filter (0.3 microns), differential pressure gauges (for the pre-filter, fine filter, and HEPA filter), lamp, fan, SOP/DOP ports, power sockets.
The fan will suck and pull the air to the HEPA filter (H14 HEPA filter), which captures the dust and particles. The HEPA-filtered air will be distributed in unidirectional form into the working Zone.
The downflow of air will carry the dust generated during powder processing into a pre-filter. After pre-filtered, the air will go through a fine filter (F8 filter) and is typically re-circulated.
The HEPA-filtered air is divided into 2 parts.
- 90% of the air flows through a diffuser and forms a vertical laminar flow into the working zone.
- 10% of HEPA-filtered air is bled out of the booth through the air outlet to maintain the working zone under negative pressure, minimizing airborne contamination breakout.
Features of Dispensing booth
Negative pressure design prevents the powder from escaping from the working zone, Unidirectional airflow provides a superior aseptic working area, and the stainless steel SUS 304 structure with rounded corners makes
dispensing (sampling or weighing) booth is hygienic, and easy to clean, and + 3-stage filtration method (pre-filter, fine filter, and HEPA filter included) provides excellent efficiency, The maximum noise level of below 65 dB, Differential pressure gauges are equipped to monitor the integrity of the filters, + PVC curtain or air curtain increases the containment efficiency.
PERFORMANCE QUALIFICATION PROTOCOL OF DISPENSING BOOTH
TABLE OF CONTENT
- Performance Qualification Protocol Approval
- Objective
- Scope
- Responsibility
- Prerequisite
- Reference
- Testing Procedure -Airflow Laminarity by Smoke Test, Non-viable particle count, Viable particle count
- Performance qualification summary and conclusion
- Abbreviation
- Performance Qualification Approval
- Particle count test report sheet
- Viable particle count test report sheet
Objective:
The objective of the protocol is to establish documentary evidence for the Open Fronted Containment Facility to demonstrate that the unit is qualified for correct operation as per the guidelines outlined in this protocol.
Scope:
This procedure applies to the performance qualification of Open Fronted Containment Facility comprising the following tests
Airflow laminarity by a smoke test
Non-viable particulate count.
Viable particle count
Responsibility:
Client:
Preparation, Review, and approval of the protocol.
Providing required support during operation and preparation of PQ report.
Execution of Viable Particle count
Supplier:
Execution of protocol & Collection of data and preparation of final PQ report.
Pre Requisite:
- Installation Qualification Documents
- Operation Qualification Documents
References:
United States Pharmacopoeia, ISO 14644
TESTING PROCEDURE
AIRFLOW LAMINARITY TEST BY SMOKE TEST
Purpose: –
The purpose of this test is to check the laminarity of Airflow which is coming through HEPA filters of the unit.
Apparatus Required: –
Rod with cotton wrapped on one end.
Video camera for a live demonstration of the activity.
Chemical required
Titanium Tetrachloride : B. N —————-
Acceptance Criteria:-
The smoke generated by the titanium tetrachloride should flow in a laminar way when the unit is in working condition.
Operating Procedure:-
Switch on the unit, one hour before taking the measurement and allow the system to stabilize.
Assure that the magnetic gauge reading is within range (10 – 20 mm).
Wrap the rod one end with cotton and dip it in the Titanium tetra chloride solution.
Now move the rod inside the OFCF area from left to right selecting three locations (upper, middle, and lower).
Cover the activity by video film.
Note: Follow safety precautions, avoiding the splashing of the reagent as it fumes densely.
Attachment: –
1. Snaps of video film
2. Video film disk
NON-VIABLE PARTICULATE COUNT
Purpose: –
The purpose of this test is to verify the cleanliness of ISO Class-5 of the Installation by ISO 14644.
Apparatus Required: –
Discrete particulate counter.
Acceptance Criteria:-
| Cumulative particle concentration per cubic meter | ||
| Particle Size | 0.5 | 5.0 |
| ISO Class-5 | 3520 | 29 |
Operating Procedure:
Set up the particle counter by the manufacturer’s instructions.
Place the discrete particle counter in the sample locations.
Position of sample probe pointing into the airflow.
Sample the volume of air.
Record the results in the test record sheet.
Attachment
Calibration certificate of Discrete particle counter.
Results Sheet
VIABLE PARTICLE COUNT
Purpose: –
The purpose of this test is to demonstrate the capability of the installation’s air handling system to maintain the viable particle count as per USP-39 through the settle plate technique and air sampler technique.
Apparatus Required: –
Settling Plate. Air Sampler
Acceptance Criteria:-
Settling Plate:
Colony forming Unit = Less than 1cfu per 90 mm Petri plate.
Air Sampler:
Colony forming Unit = Less than 3cfu per cubic meter of air.
Operating Procedure:-
Settle Plate technique:
Switch on the unit, one hour before taking the measurement and allow the system to stabilize.
Assure that the Magnehelic gauge reading is within range (10 – 20 mm).
Keep the settling plate at the ‘3’ location as defined in the drawing.
Expose the plate for ‘1’ hour.
Analyze the plate for Microbiological analysis.
Air Sampler technique:
Switch on the unit, one hour before taking the measurement and allow the system to stabilize.
Assure that the Magnehelic gauge reading is within range (10 – 20 mm).
Start the Air sampler as per its operational manual
Sample the air at the center of the LAF safe zone by setting the air sampling rate at 6m3/hr and sampling time =10 min.
Take the filter and analyze the plate for Microbiological analysis
Note: Sampling shall be taken for ‘3’ consecutive days
Sample Location for Settle plate:
Attachment: –Results Sheet.
Performance Qualification Summary and Conclusion:
Performance Qualification Approval
The performance qualification documents are studied and approved by the Undersigned Authorized Personnel.
The approved Performance Qualification supersedes all the previously agreed specifications.
Report Preparation and Review:
Report Approval:
Pharma More Jobs and post Please click here