IMPURITIES IN NEW DRUG SUBSTANCES To provide guidance for registration applications on the content and qualification of impurities in new drug substances produced by chemical syntheses and not previously registered in a region or member state Impurities in new drug substances are addressed from two perspectives: Chemistry Aspects include classification …
Read More »Failure Mode Effect Analysis (Risk Assessment) Compression Stage
Failure Mode Effect Analysis (Risk Assessment) Compression Stage For More Pharma Updates Visit -https://pharmaguidances.com
Read More »Process validation scheme
Process validation scheme Traditional process validation Where validation data on production-scale batches are not provided with the application and traditional process validation is proposed, the process validation scheme described below should be submitted by the applicant. This should outline the formal process validation studies to be conducted on production-scale batches …
Read More »Process validation (Continuous process verification) for finished products
Process validation (Continuous process verification) for finished products Process validation can be defined as documented evidence that the process, operated within established parameters can perform effectively and reproducibly to produce a medicinal product meeting its predetermined specifications and quality attributes (ICH Q7). Continuous process verification has been introduced to cover …
Read More »Qualified Person
Qualified Persons A qualified person shall be in possession of a diploma, certificate, or other evidence of formal qualifications awarded on completion of a university course of study, or a course recognized as equivalent by the Member State concerned, extending over a period of at least four years of theoretical …
Read More »DRUG DESIGN (AN OVERVIEW)
DRUG DESIGN (AN OVERVIEW) DRUG DESIGN DRUG DESIGN Approaches to drug discovery: Serendipity (luck) Chemical Modification Screening Rational Irrational, based on serendipity & Intuition Trial & error approach in DRUG DESIGN Time consuming with low through output No de novo design, mostly “Me Too Approach” First generation Rational approach in …
Read More »CHANGE CONTROL
CHANGE CONTROL Change Control is “A formal system by which qualified representatives of appropriate disciplines review proposed or actual changes that might affect the validated status of facilities, systems, equipment or processes. The intent is to determine the need for action that would ensure and document that the system is …
Read More »Quality Management System
Quality Management System Definition: A Quality Management System is a collection of policies, procedures, plans, resources, processes, practices, and the specification of responsibilities and authority of an organization designed to achieve product and service quality levels, customer satisfaction, and company objectives. Documentation: Quality Policy – describes the organization’s approach to …
Read More »GUIDE TO INSPECTIONS OF HIGH PURITY WATER SYSTEMS
GUIDE TO INSPECTIONS OF HIGH PURITY WATER SYSTEMS I. SYSTEM DESIGN For parenteral products where there is a concern for pyrogens, it is expected that Water for Injection will be used, This applies to the formulation of products, as well as to the final washing of components and equipment used …
Read More »HAZARD ANALYSIS OF CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP)
HAZARD ANALYSIS OF CRITICAL CONTROL POINT (HACCP) TABLE OF CONTENTS HAZARD ANALYSIS OF CRITICAL CONTROL POINT 1. Declaration. Quality Policy Quality Objectives Company Profile Layout of Plant Organization Chart HACCP Introduction HACCP Prerequisite Programs Seven Principles of HACCP Hazards HACCP Scope HACCP Team Responsibility Hazard Analysis Introduction Hazard Analysis for …
Read More »Interview Questions & Answers (Quality Assurance)
Interview Questions & Answers (Quality Assurance) 1.What is Quality Assurance : Quality Assurance is a deep concept covering all matters that individually or collectively influence the quality of a product. It is the complete & whole of the arrangements made with the object of ensuring that the manufactured products are of …
Read More »OOS (Out of Specification) As PER USFDA & MHRA
OOS (Out of Specification) Definition: It is defined as those results of the in-process or Finished which has been sed products testing, which falling out specified limit or acceptance Criteria which has been specified in the official Monograph or Product registered Specification. OOS was found due to the following reasons: …
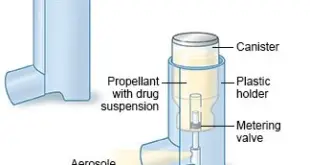
Read More »SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF METERED – DOSE INHALERS (MDI)
SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF METERED–DOSE INHALERS (MDI) General .– Manufacture of Metered-Dose-Inhalers shall be done under conditions which shall ensure minimum microbial and particulate contamination. Assurance of the quality of components and the bulk product is very important. Where medicaments are in suspended state, uniformity of suspension shall be established. …
Read More »SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF TOPICAL PRODUCTS
SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF TOPICAL PRODUCTS i.e. EXTERNAL PREPARATIONS (CREAMS, OINTMENTS, PASTES, EMULSIONS, LOTIONS, SOLUTIONS, DUSTING POWDERS, AND IDENTICAL PRODUCTS). The entrance to the area where topical products are manufactured shall be through a suitable airlock. Outside the airlock, insectocutors shall be installed. The air to this manufacturing area …
Read More »Environmental Monitoring
Environmental Monitoring – All environmental parameters listed under para 3.1 to 3.10 shall be verified and established at the time of installation and thereafter monitored at periodic intervals. The recommended frequencies of periodic monitoring shall be as follows: ( a ) Particulate monitoring in air – 6 Monthly (b) HEPA …
Read More »SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF ORAL LIQUIDS (SYRUPS, ELIXIRS, EMULSIONS AND SUSPENSIONS)
SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF ORAL LIQUIDS (SYRUPS, ELIXIRS, EMULSIONS AND SUSPENSIONS) Building And Equipment – The premises and equipment shall be designed, constructed, and maintained to suit the manufacturing of Oral Liquids. The layout and design of the manufacturing area shall strive to minimize the risk of cross-contamination and …
Read More »SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF ORAL SOLID DOSAGE FORMS (TABLETS AND CAPSULES)
SPECIFIC REQUIREMENTS FOR MANUFACTURE OF ORAL SOLID DOSAGE FORMS (TABLETS AND CAPSULES) The processing of dry materials and products creates problems of dust control and cross-contamination. Special attention is, therefore, needed in the design, maintenance, and use of premises and equipment in order to overcome these problems. Wherever required, enclosed …
Read More »Documentation for Manufacture of Sterile products
Documentation for Manufacture of Sterile products The manufacturing records relating to manufacture of sterile products shall indicate the following details: – (1) Serial number of the Batch Manufacturing Record. (2) Name of the product. (3) Reference to Master Formula Record. (4) Batch / Lot number. (5) Batch / Lot size. …
Read More »In-process Checks during Tertiary Packaging Operations
In-process Checks during Tertiary Packaging Operations of cartons/ shrink-wrapped units in one corrugated box / LDPE bag: Count the no. of cartons / shrink wrapped units in one corrugated box / LDPE bag and verify with the Batch Packing Record. Stencil on corrugated boxes: Check the stencil details on the …
Read More »In-process Checks during Secondary Packaging Operations
In-process Checks during Secondary Packaging Operations Performed in In-process quality checks as pre-defined frequency in BPR and to be sorted out the strips/blister with below-mentioned tablet defects before packed in carton or during Packing Broken Tablets Laminated Tablets Chipped Tablets Discoloured Tablets With Black particles Tablets With foreign particle Tablets …
Read More »