Interview Questions & Answers (Quality Assurance)
1.What is Quality Assurance :
Quality Assurance is a deep concept covering all matters that individually or collectively influence the quality of a product. It is the complete & whole of the arrangements made with the object of ensuring that the manufactured products are of the quality required for their intended use.
2. Responsibility of Quality Assurance:
In process checks during manufacturing & packing activities, Providing Line clearance in Manufacturing, Packaging and Warehouse, Sampling of products in manufacturing and packing, Reviewing the manufacturing and packing batch record, Issuance of documents to other departments, calibration of Instruments, Providing training to other department, Ensuring online documentation and compliance throughout the plant,Review & approve Standard operating procedure, change controls and deviations.
3. What is tablet :
Tablets is defined as the solid unit dosage form of medicines with suitable excipients and prepared either by molding or by compression. It comprises a mixture of active substances and excipients, usually in powder form, pressed or compacted from a powder into a solid dose.
4. Name any three tablet processing problems :
Mottling, Capping, lamination, picking and sticking
Mottling- unequal colour distribution of a tablet.
Capping- Partial or complete separation of a tablet top or bottom crowns.
Lamination- Separation of tablets into two or more layers.
picking- Because of adhesion to the punch faces, Localized portion missing on the surface of the tablet.
Sticking- Adhesion of tablet localized portion to the punch faces resulting in rough and dull appearance.
5. What is Disintegration Test :
It is the time required for the Tablet / Capsule to break into particles, the disintegration test is a measure of the time required under a given set of conditions (Temperature) for a group of tablets/capsules to disintegrate into particles.
Cycle of shaft holding the tube basket limit is 29-32 cycles per minutes and distance covered by shaft basket is 50-60 mm and beaker temperature is 35 to 39 º C.
Disintegration is to be Performed to determine whether tablets or capsules disintegrate within the prescribed time when placed in a liquid medium at the experimental conditions.
6. What are the Disintegration Time of tablets :
- Uncoated Tablet 15 min as per BP
- Uncoated Tablet 30 min as per USP
- Sugar Coated Tablet 60 min as per BP
- Film Coated Tablet 30 min as per BP
- Plain Coated Tablets DT in specific medium for 30 min as per USP
- Enteric Coated Tablets DT in simulated gastric fluid (0.1 M HCl) for 1 hr and then in simulated intestinal fluid (Phosphate buffer 6.8 pH) until disintegrate as per USP.
- Dispersible Tablets 3 min ( 15- 25º C ) as per BP.
- Effervescent Tablets 1 tablet in 200 mL water for 5 min ( 15- 25º C )
- as per BP
- Buccal Tablets 4 hrs as per USP.
- Soluble Tablets 3 min ( 15- 25º C ) as per BP.
- Chewable Tablets are not require to comply with test
7. What are the Disintegration Time of capsules:
- Gastro resistant capsule DT 2 hrs without disk in 0.1 M HCl and phosphate buffer pH 6.8 for further 60 min as per BP.
- Hard and Soft gelatin capsule DT 30 min as per BP & USP.
8. What is Friability Test of Tablet & friability calculation :
Friability is defined as the percentage of weight loss of powder from the surface of the tablets due to mechanical action and the test is performed to measure the weight loss during transportation.
Friability (%) =W1– W2/W1X100
Where,
W1 = Weight of Tablets (Initial / Before Tumbling) &
W2 = Weight of Tablets (After Tumbling or friability)
Limit : Friability (%) = Not More Than 1.0 %
Tablets with individual weight equal to or less than 650 mg then take the sample of whole corresponding to as near as 6.5 gram equivalent and tablets with individual weight more than 650 mg then take sample of 10 whole tablets to perform friability test. Tablets must be de-dusted prior to and after use.
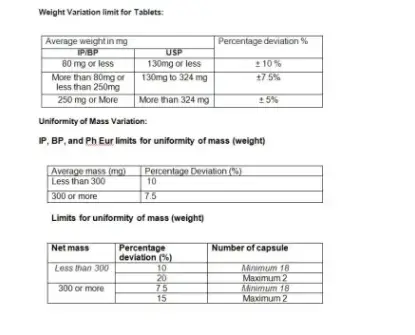
9. Weight Variation limit for Tablets and Uniformity of Mass Variation:
10. What is Validation :
Documented program or evidence, that provides a high degree of assurance that a specific process method or system consistently produce a result indicating predetermined accepted criteria.
11. What is Validation Protocol :
A written plan starting how validation will be conducted and identifying specific acceptance criteria. For example the protocol for a typical manufacturing process identifies processing equipment’s, critical process parameters/ operating ranges, Critical Quality attributes and product characteristics. Sampling and test data to be collected, number of validation runs and acceptable test results.
12. Prospective Validation :
Establishing documented evidence that a system dos what it suppose to do prior to the commercial distribution of the new product or an existing product made by a new or modified process.
13. Retrospective Validation :
Establishing documented evidence that a system does what it purports to do based on a review and analysis of historic information. It is normally conducted on the drug material already being commercially distributed and is based on accumulated production, testing and control data.
14. What is Calibration :
The demonstration that a particular instrument or device produces results within specified limits by comparison with those produced by a traceable standard over an appropriate range of measurements.
15. What is Qualification :
The action of proving that any equipment or process work correctly and consistently and produces the expected result. Qualification is part of, but not limited to a validation process, i.e. Installation Qualification (IQ), Operation Qualification(OQ) and Performance Qualification (PQ).
The act of planning, carrying out and recording the results of tests on equipment to confirm its capabilities and to demonstrate that it will perform consistently as intended use and against predefined specification.
16. What is User Requirement Specification :
A requirement specification that describes what the equipment or the system is supposed to do, thus containing at least a set of criteria or condition that have to meet.
Detailed design & functional specifications shall be taken from the supplier for a particular piece of equipment / instrument / system / facility. The same shall be prepared by User & reviewed by Engineering & Quality Assurance. Based on the specifications, URS document shall be prepared
17. What is Factory Acceptance Test :
A Factory Acceptance Test is usually preformed at the vendor prior to shipping to a client. The vendor tests the system in accordance with the clients approved test plans and specifications to show that system is at a point to be installed and tested on site.
18. What is Site Acceptance Test :
A Site Acceptance Test the system is tested in accordance to client approved test plans and specifications to show the system is installed properly and interfaces with other systems and peripherals in its working environment.
19. Design Qualification :
Documented verification that equipment, instrument, facility and system are of suitable design against the URS and all key aspects of design meet user requirements.
20. Installation Qualification (IQ) :
The documented verification that all components of the equipment and associated utilities are properly installed or modified in accordance with the approved design and manufacturer’s recommendations.
21. Operational Qualification :
Operational qualification consists of verification and documentation, of the parameters of the subjected equipment. The documented verification that the equipment, instrument, facility and system as installed or modified, perform as intended throughout the installed operating range.
22. Performance Qualification :
Performance Qualification is designed to prove the process, can consistently produce a product that meets the stated requirements and specifications. It is a documented verification that the equipment, instrument, facility and system as connected together, can perform effectively and reproducibly, based on the approved process method and product specification.
23. Why Three consecutive batches taken for Validation :
Consecutive meaning following closely with no gap or following one after another without interruption.
- The number of batches to be taken under validation depends upon the risk involved in the manufacturing Critical process parameters & critical Quality Attribute so depends upon that manufacturer have to choose the number of batches to be validated.
- If we will consider less than two batches then the data will not be sufficient for evaluation of and to prove reproducibility of data between batch to batch variation & if we consider more than three batches it can increase the time & cost of manufacturer which usually not preferred.
- Generally if we will require quality in the First batch, then it is accidental (co-incidental), Second batch quality is regular & third batch quality is Validation or Confirmation.
- Statistical evaluation cannot be done by considering two points, because two points always draw a straight line so minimum three points required for comparison of data.
24. In A Oral solid dosage Manufacturing Facility ‘positive’ Pressure is Maintained In Processing Area or Service Corridors :
In tablet manufacturing facilities, pressure gradients are maintained to avoid cross contamination of products through air. Usually processing areas are maintained under positive pressure with respect to service corridors.
25. What is Positive Pressure :
Atmospheric pressure which is higher than the immediate surrounding areas usually measured in inches of water or Pascal.
26.What is Cross Contamination :
Contamination of a material or product with another material or product is called cross contamination.
27. What is Schedule -M :
Good manufacturing practice and requirements of the Premises of the plant, Waste disposal and equipment’s. GMP has two parts Part I and Part II
Part I is GMP for Factory Premises and Part II is GMP for Plant & equipment’s.
28. What is Quarantine in pharmaceuticals :
The status of the materials isolated physically or by other effective means, pending for a decision on their subsequent use. Materials are kept in Quarantine area with proper status labeling.
29. What is Relative Humidity :
It is the ratio between the actual amount of water vapour present in certain volume of air at a given temperature and the maximum amount of water vapour that the air can retain at that temperature.
30. Expiry/Expiration Date :
The date usually placed on the containers /labels of material designating the time during which the material is expected to remain within the established self life specifications if stored under defined conditions and after which it should not be used.
31. What is Deviation:
Any unwanted event that represents a departure from approved processes or procedures or instruction or specification or established standard or from what is required. Deviations can occur during manufacturing, packing, sampling and testing of drug products.
Examples of Deviations: Temperature and RH of area goes out of limit during manufacturing, Typographical error observed in approved documents, Standard operating procedure not followed, Breakdown of equipment, Spillage of material during unloading, Instrument calibration results goes out of limit etc. Deviations are of three types Minor, Major and Critical
32. What is Change Control :
It is a Approved Procedure which is taken to change in any documents, Standard operating procedures, Specification, Process parameters and change in batch size etc. Change control is raised by user department as per requirement and finally the change control is approved by Quality assurance. Change control can be raised through software or through manually.
After Final approval of change control the changes can be made in documents and change control can be closed after completion of required action plan which is mentioned in the Change control form.
Change controls are of two types i.e Major and Minor.
33. Corrective action :
An action taken to eliminate the cause of the existing deviation , incident or problem in order to prevent its recurrence (occurring again).
34. Preventive action:
An action taken to eliminate the cause of potential deviation, incident or problem in order to prevent its occurrence (an incident or event).
35. What is Hold Time Study :
Hold Time studies establish the time limits for holding the materials at different stages of production to ensure that the quality of the product does not degrade significantly during the hold time at a required temperature and Relative Humidity.
36. What is Site Master File :
A Site Master File (SMF) is a document that describes the structure of the organization which includes the site, the manufacturing activities carried out, the facility and premises, number of employee with their Qualification, Production system, Quality Control System and also details of the quality management system which are in place.
It contains General information about the plant, Quality System, Personnel, Premises and Equipments, Production system, Documentation, Quality Control system, Self Inspection and site inspection history etc.
37. What is VMP :
A Validation Master Plan is a document that summarizes the firm’s/organizations overall philosophy, intentions and approach to be used for establishing performance adequacy. It provides information on the firms/organizations validation work programme and defines details of and timescales for the validation work to be performed, including a statement of the responsibilities of those implementing the plan.
It contains the validation policy, Process & Cleaning validation, Qualification & Requalification, Computer validation, Utility validation & Qualification, Vendor Qualification , Temperature mapping, Change control, Deviation, Risk Assessment, Standard Operating procedure, Training, Area Qualification, calibration and Preventive maintenance & closure of VMP etc. VMP Shall be updated yearly.
38. What is Control Sample :
An appropriately identified sample that is representative of each batch that shall be retained is known as control sample. These are also referred as retention or reference sample.
The control sample shall be collected at the initial, middle and at the end of packing operation of the batch and the details of the total pooled quantity collected shall be entered in the respective Batch Packing Records with sign, date & sample collection time.
39. How much sample to be collected for Control or Reference Sample :
The control sample should consist of twice the quantity required for complete analysis and Sample quantity shall be decided on the basis of specifications given by Quality Control.
Control sample shall be collected for Raw material, Packing Material and Finished Products
40. What are the tools used for Investigation in Pharmaceuticals :
The tools are Brain Storming,Fish Bone diagram, 5 Why, Affinity Diagram or Chart, Root cause analysis, Failure Mode Effect Analysis etc.
41.What is Cleaning Validation :
It is a documented evidence which provides us the assurance that a cleaning procedure is consistently removing product residue from equipment.
Three batches shall be taken for Cleaning validation After the Cleaning procedure for the equipment’s are validated, periodic monitoring / Cleaning verification shall be done once in year on worst case product
42. What is Worst case in cleaning validation :
The product selected from a group of products that represents a greater risk of carry over the residue of previous product to next product manufactured using the same equipment by virtue of its solubility, Cleanability, Permitted daily dosage exposure, toxicity or a combination of these factors, therapeutic dose, etc.
It is the case or condition where there is a chances of Product failure.
43. What is Line clearance :
Line clearance is a process which provides a high degree of confidence or assurance that the said line or area is free from any unwanted residue or left over of previous processing’s before proceeding for next process. Quality assurance has to provide Line clearance before the start of any activity whether it is batch to batch change over and Product to product change over.
Line clearance shall be given by Quality Assurance at Raw material Dispensing stage, Manufacturing stage, Packing stage and in Quality Control before start of any activity.
44. Water Validation Phases :
Water system validation has been categorized into 3 phases: Phase I, Phase II and Phase III.
Phase I Requires a 2 – 4 weeks (14 days minimum) testing period in order to monitor the system deeply.
Phase II is continuity of previous phase i-e phase I, it carries the sampling plan same as previous phase plan & it also facilitates the monitoring of system for 2 – 4 weeks (30 days) period.
In phase III sampling locations and frequency reduced as compared to previous phases. Phase III represents that the water system shows reliable under control attainment over such a long time period & Phase III typically runs for one year after the satisfactory completion of phase II.
45. What is Concurrent Validation :
Concurrent validation is used to establish documented evidence that a facility and process will perform as they are intended, based on information generated during actual use of the process.
46. What is Product Recall & Mock Recall :
A product recall is a request from a manufacturer to return or removal of a marketed product after the discovery of safety issues or product defects that might endanger the consumer or put the maker/seller/ manufacturer at risk of legal action.
Mock means Make a Duplicate or exact copy of something.
Mock recalls are routine exercises conducted by manufacturers, processors, distributors and other various trading partners in the supply chain to assess or verify their recall procedures and responsiveness and to train the recall team.