Glycerin: Properties, Applications, and Benefits
Glycerin, also known as glycerol or glycerine, is a versatile and widely used chemical compound with a range of applications in various industries. It is a colorless, odorless, and viscous liquid that has gained popularity due to its unique properties and beneficial characteristics. In this blog post, we will explore the properties, applications, and benefits of glycerin.
Understanding Glycerin
Chemical Properties:
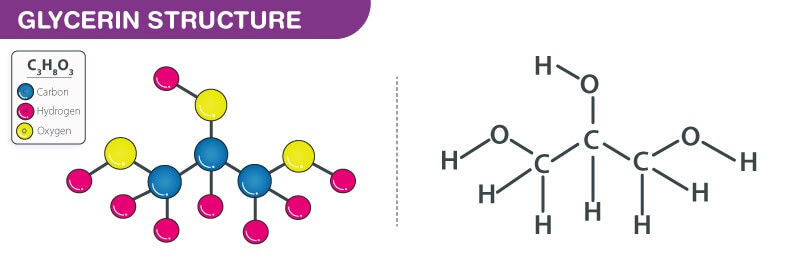
Composition: Glycerin is a triol, meaning it contains three hydroxyl groups. Its chemical formula is C3H8O3.
Solubility and Viscosity: Glycerin is highly soluble in water and exhibits high viscosity, which gives it its characteristic syrupy texture.
Production Methods:
Natural Sources: Glycerin can be derived from natural sources, such as vegetable oils and animal fats, through a process called saponification.
Synthetic Production: Glycerin can also be produced synthetically through the hydrolysis of epichlorohydrin or the fermentation of sugars.
Applications of Glycerin
Food and Beverage Industry:
Sweetener and Humectant: Glycerin is used as a sweetener and humectant in various food and beverage products, providing sweetness and moisture retention.
Food Processing Aid: It is utilized as a processing aid in food manufacturing to improve texture, prevent crystallization, and extend shelf life.
Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products:
Excipient in Pharmaceuticals: Glycerin serves as an excipient in pharmaceutical formulations, helping to improve the stability, solubility, and viscosity of drugs.
Skincare and Cosmetics: It is used in skincare and cosmetic products for its moisturizing, emollient, and humectant properties.
Industrial Applications:
Chemical Intermediary: Glycerin is used as a raw material in the production of various chemicals, including solvents, surfactants, and polyols.
Lubricants and Antifreeze: It finds applications in lubricants, hydraulic fluids, and antifreeze formulations due to its viscosity and thermal stability.
Sorbitol Solution: Properties, Uses, and Applications
Benefits and Sustainability of Glycerin:
Moisturizing and Hydrating Properties:
Skincare Benefits: Glycerin’s humectant properties help attract and retain moisture, making it effective in moisturizing and hydrating the skin.
Haircare Benefits: It can also be used in haircare products to improve moisture retention and promote softness and manageability.
Environmentally Friendly:
Biodegradability: Glycerin is readily biodegradable, meaning it can be broken down by natural processes without causing harm to the environment.
Renewable Sources: Glycerin can be derived from renewable sources, such as plant-based oils, contributing to sustainability efforts.
Health and Safety:
Non-Toxicity: Glycerin is generally recognized as safe for consumption and topical use, with a low risk of toxicity or adverse effects.
Hypoallergenic: It is considered hypoallergenic, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies.
Regulatory Considerations
Food and Drug Administration (FDA):
GRAS Status: Glycerin has Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) status from the FDA for its use in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Labeling Requirements: Products containing glycerin must adhere to FDA labeling guidelines for accurate ingredient declaration.
European Union (EU) Regulations:
European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.): Glycerin is listed in the Ph. Eur. as an excipient for pharmaceutical use, specifying its quality and purity requirements.
European Cosmetics Regulation: Glycerin is permitted for use in cosmetics and personal care products in compliance with EU regulations.
Conclusion
Glycerin is a valuable compound with a wide range of applications in various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, personal care, and industrial sectors. Its unique properties, such as its moisturizing ability, humectant properties, and non-toxic nature, make it a preferred ingredient in many formulations. Understanding the properties, applications, benefits, and regulatory considerations of glycerin is crucial for manufacturers, formulators, and consumers alike. By harnessing the benefits of glycerin and adhering to regulatory guidelines, the industry can develop innovative products that promote health, sustainability, and overall well-being. As the demand for natural and sustainable ingredients continues to grow, glycerin remains a versatile and reliable component in formulating products that cater to the needs of consumers while delivering effective results.
