Best Practices in the Validation of Pharmaceuticals: Ensuring Quality, Safety, and Compliance
In the pharmaceutical industry, validation plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. Validation is a systematic process that involves establishing documented evidence, using scientific principles and statistical methods, to demonstrate that a process, system, or method consistently produces results that meet predetermined specifications. In this comprehensive blog post, we will delve into the world of validation in pharmaceuticals, exploring its importance, key elements, regulatory requirements, and best practices. Join us on this journey to discover how robust validation practices contribute to the successful development, manufacturing, and distribution of safe and effective pharmaceutical products.
Importance of Validation of Pharmaceuticals:
Define validation in the context of the pharmaceutical industry and its significance in ensuring product quality, safety, and efficacy.
Highlight the essential role of validation in meeting regulatory requirements and gaining marketing authorization from health authorities.
Process Validation: Discuss the validation of manufacturing processes to ensure consistent and reliable production of pharmaceutical products.
Analytical Method Validation: Explain the validation of analytical methods used for testing the quality and purity of pharmaceutical products.
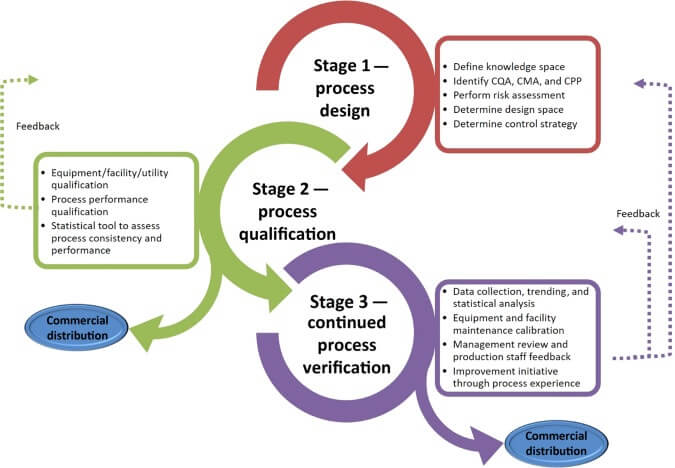
- Validation Life Cycle and Stages:
Validation Life Cycle: Describe the stages involved in the validation process, including planning, qualification, process validation, and continued process verification.
- Regulatory Requirements for Pharmaceutical Validation
- FDA Requirements for Pharmaceutical Validation:
cGMP and Validation: Explore how current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) regulations by the FDA mandate validation as a key component of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
FDA Guidance Documents: Discuss relevant FDA guidance documents related to validation, such as Process Validation: General Principles and Practices.
- EMA and Other Regulatory Authorities:
European Medicines Agency (EMA): Explain EMA’s expectations for pharmaceutical validation and alignment with international guidelines.
Other Global Regulatory Authorities: Highlight the expectations of other regulatory authorities, such as Health Canada and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan, regarding pharmaceutical validation.
III. Best Practices in Pharmaceutical Validation
- Validation Master Plan (VMP):
Importance of VMP: Discuss the significance of developing a comprehensive VMP that outlines the validation approach for all critical processes and systems.
Components of VMP: Explore the key components of a VMP, including validation strategies, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Risk-Based Approach to Validation:
Principles of Risk-Based Validation: Explain the principles of risk-based validation, focusing resources on critical areas that pose the highest risks to product quality and patient safety.
Risk Assessment Methods: Discuss various risk assessment tools, such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP).
- Design Qualification (DQ):
Purpose of DQ: Explore the role of design qualification in ensuring that equipment, systems, and facilities are designed to meet intended requirements.
DQ Process: Explain the steps involved in conducting design qualification, including design specification, installation, and functionality testing.
- Installation Qualification (IQ):
IQ Objectives: Discuss the objectives of installation qualification, which involves verifying that equipment and systems are correctly installed and meet specified requirements.
IQ Protocols and Execution: Explain the preparation of IQ protocols and the execution of installation tests and verifications.
- Operational Qualification (OQ):
OQ Requirements: Describe the requirements of operational qualification, which involves verifying that equipment and systems operate within specified limits.
OQ Protocols and Execution: Explain the preparation of OQ protocols and the execution of operational tests and performance qualifications.
- Performance Qualification (PQ):
Purpose of PQ: Discuss the significance of performance qualification in demonstrating that processes consistently produce products that meet predetermined specifications.
PQ Protocols and Execution: Explain the preparation of PQ protocols and the execution of process performance tests.
- Analytical Method Validation:
Importance of Analytical Method Validation: Discuss the criticality of validating analytical methods to ensure the accuracy, reliability, and precision of test results.
Method Validation Parameters: Explain the parameters considered in analytical method validation, such as specificity, accuracy, precision, linearity, and robustness.
- Continued Process Verification (CPV) and Continued Method Verification (CMV)
- CPV in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing:
CPV Objectives: Discuss the purpose of CPV in pharmaceutical manufacturing, which involves monitoring and evaluating processes to ensure ongoing product quality.
Statistical Process Control (SPC): Explain the use of statistical tools and techniques in CPV, such as control charts and trend analysis.
- CMV in Analytical Testing:
CMV Objectives: Describe the objectives of CMV in analytical testing, which involves ongoing verification of analytical methods to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Stability Indicating Methods: Discuss the importance of stability-indicating methods in CMV to detect potential changes in product quality over time.
- Validation of Computer Systems
- Importance of Computer System Validation (CSV):
CSV in the Pharmaceutical Industry: Explore the criticality of validating computer systems used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, testing, and data management.
21 CFR Part 11 Compliance: Explain the requirements of 21 CFR Part 11, which governs electronic records and electronic signatures.
- CSV Process and Documentation:
CSV Lifecycle: Discuss the stages involved in computer system validation, including user requirements, design, testing, and maintenance.
Validation Documentation: Explain the documentation required for computer system validation, including validation plans, risk assessments, and test scripts.
- Validation Change Control and Deviation Management
- Change Control in Validation:
Change Control Process: Discuss the importance of change control in managing changes to validated processes, systems, and methods.
Impact Assessment: Explain how change control includes evaluating the impact of changes on product quality and patient safety.
- Deviation Management in Validation:
Deviation Handling Process: Explore the process of managing deviations that occur during validation activities.
Investigation and Corrective Actions: Explain how deviations are investigated, and appropriate corrective and preventive actions are implemented.
VII. Training and Qualification of Personnel
- Personnel Training:
Importance of Training: Discuss the criticality of training personnel involved in validation activities to ensure their competency and adherence to procedures.
Training Records: Explain the importance of maintaining detailed training records to demonstrate compliance with training requirements.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, validation is a foundational process in the pharmaceutical industry that ensures the quality, safety, and efficacy of pharmaceutical products. By adopting best practices in validation, pharmaceutical companies can comply with regulatory requirements, meet quality standards, and gain the trust of patients and healthcare providers. With a risk-based approach, robust validation master plans, and continual process verification, pharmaceutical companies can navigate the complexities of validation and deliver safe and effective medications to patients worldwide. Embracing validation as an integral part of the pharmaceutical development and manufacturing process will help pave the way for innovation, continuous improvement, and the advancement of global healthcare.