QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IN PHARMA
A QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN PHARMA (QMS) is a formalized system that documents processes, procedures, and responsibilities for achieving quality policies and objectives. A Quality Management system in Pharma helps coordinate and direct an organization’s activities to meet customer and regulatory requirements and improve its effectiveness and efficiency on a continuous basis. The ICH Q10 guideline describes a comprehensive model for an effective Quality Management system in Pharma for the pharmaceutical industry, referred to as the Pharmaceutical Quality System (PQS). It applies to the development and manufacture of pharmaceutical drug substances and medicines, including biotechnology and biological products, throughout the product lifecycle and has been adopted by regulators worldwide, including EMA and FDA. The Quality Management system in Pharma “assures that the desired product quality is routinely met, suitable process performance is achieved, the set of controls are appropriate, improvement opportunities are identified and evaluated, and the body of knowledge is continually expanded.”(ICH Q10, Section 3.1.3 Commercial Manufacturing)
Principle of the Quality Management System in Pharma:
The principle of the pharmaceutical quality system (PQS), formerly called Quality Management system in Pharma (QMS), is to ensure medicinal products are:
- Fit for their intended use
- Comply with relevant authorization requirements
- Do not place patients at risk due to inadequate safety, quality, or efficacy
To comply, the Quality Management system in Pharma should incorporate GMP and Quality Risk Management (QRM) principles and be:
- Designed comprehensively
- Documented fully
- Implemented correctly
- Monitored for effectiveness
- Adequately resourced and fully supported by senior management.
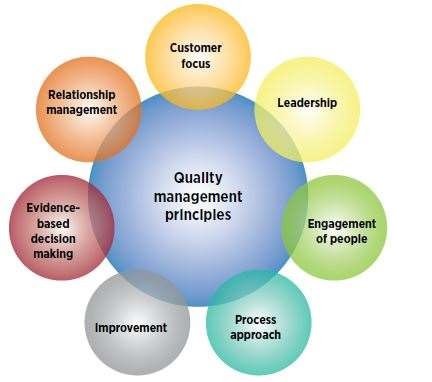
Seven quality management principles
The ISO 9001 Quality Management System is based on seven principles, each one a critical focus for a system QMS. These seven principles are Customer focus. In order for the QMS to succeed, top management needs to provide resources and an adequate ongoing review of the system. The people who work at your organization are the most important asset, and their knowledge and experience need to be understood in the QMS. A company will only survive if it gets better over time, so the QMS needs to focus on finding ways to do things better. Proper management cannot be done if we don`t know how a process is actually working. By basing our decisions on facts, we can better manage and improve the QMS. In order to make this work, we need to manage the relationship between ourselves and our suppliers.
BENEFITS OF QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS IN PHARMA
| Implementing a quality management system affects every aspect of an organization`s performance. Benefits of a documented quality management system include: Meeting the customer`s requirements, which helps to instill confidence in the organization, in turn leading to more customers, more sales, and more repeat business Meeting the organization’s requirements, which ensures compliance with regulations and provision of products and services in the most cost- and resource-efficient manner, creating room for expansion, growth, and profit These benefits offer additional advantages, including: Defining, improving, and controlling processes Reducing waste Preventing mistakes Lowering costs Facilitating and identifying training opportunities Engaging staff Setting organization-wide direction Communicating a readiness to produce consistent results. |
ELEMENTS OF A QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM IN PHARMA
Each element of a quality management system helps achieve the overall goals of meeting the customers` and organization`s requirements. Quality management systems should address an organization`s unique needs; however, the elements all systems have in common include: The organization`s quality policy and quality objectives Quality manual Procedures, instructions, and records Data management Internal processes Customer satisfaction from product quality Improvement opportunities Quality analysis
Pharmacokinetic Principles
Management shall be responsible for the Quality Management system in Pharma :
Ensuring an effective Quality Management system in Pharma is in place to achieve the quality objectives roles, responsibilities, and authorities are defined, communicated, implemented throughout the company, and Management shall determine, and provide adequate and appropriate resources (Human, financial, materials, facilities, equipment) to implement, maintain the Quality Management System applied to a specific product, process, or site and continually improve its effectiveness.
DEFINITIONS
CAPA: stands for Corrective action and preventive action, CAPA is a fundamental management tool that should be used in every quality system, It focuses on the systematic investigation of the root causes of identified problems or identified risks in an attempt to prevent their recurrence (for corrective action) or to prevent occurrence (for preventive action).
OOT (Out of trend): The test results that may be within specification but show significant Variation from the historical results.
OOS (out of specification): is defined as a result that falls outside the predetermined specifications or established acceptance criteria set by the manufacturer and/or the laboratory.
Management review of the Quality Management system in Pharma
The following activities should be conducted to manage and continually improve the Quality Management System. Management shall conduct a review of process performance. Product quality and Quality systems at every six Months (Tolerance frequency: +30 days) interval or as and when required. The review shall include (but not be limited to):
Review of previous Quality Management System review meeting observation and Compliance.
Measurement of achievement of Quality Management System objectives.
Assessment of performance indicators that shall be used to monitor the effectiveness of processes within the Quality Management System, such as:
Change control. Market Complaint, Deviation, Incident, OOS, OOT, QRM, Vendor Qualification, Stability Studies, Validation, Training, and CAPA.
Feedback on outsourced activities like any concerns related to contract laboratory, calibration services, validations, vendors, etc.
Internal quality audit processes including risk assessments, trending, etc.
External assessments such as regulatory inspections, customer audits, findings, and CAPA are taken.
Monitoring of Internal and External Factors that shall have an Impact on the Quality Management System Factors monitored by management can include:
Emerging regulations, guidance, and quality issues can have an impact on the Quality Management System.
Changes in business environment and objectives.
Outcomes of Management Review and Monitoring:
The outcome of a management review of the quality system and monitoring of internal and external factors can include:
Improvements to the quality system and related processes.
Allocation or re-allocation of resources and/or personnel training.
Revisions to quality policy and quality objectives, if required.
Agenda shall be prepared, if required any modification shall be done based on the requirement of the meeting. The agenda shall be prepared by the QA manager, reviewed, and Approved by Head QA.
Approved scanned copy of the agenda shall be circulated to respective Heads of the departments through email at least 7 days prior to the Management Review Meeting.
A list of proposed actions from the management review meeting shall be prepared in the quality management review report.
Based on the review report, observations, and recommendations, CAPA shall be defined which shall be monitored and closed.
These proposed actions / CAPA shall be recorded in the CAPA Register for further tracking and implementation.
Quality Management System review report, comprising the results of the management review, actions and recommended CAPA, and requirement of appropriate resources, for effective management of the quality system, shall be communicated to senior management.
The Plant Head and Head of Quality shall review the Quality Management System review.
During regulatory / customer audit, Quality Management System Review Agenda, Quality Management Review Report, and Quality Management System review report-CAPA Closure shall be presented to the auditor on request. Management Review Meeting Presentation and Data) is confidential.
ATTACHMENTS
Quality Management System review report
Quality Management System Review Report – CAPA Closure
Template for Quality Management System Review Agenda
Template for Management Review Meeting Presentation and Data