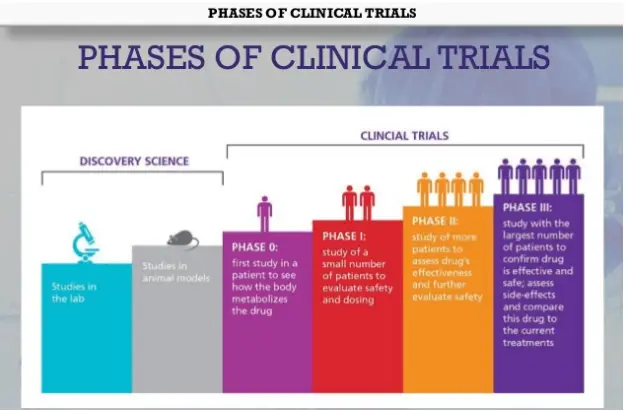
Phases of clinical trials
Contents
• Introduction:Clinical research
• Drug development phases
• Pre-Phase 1 activities
• Phases of Clinical trial
• Regulatory approvals: IND & NDA
• Summary of Clinical trial phases
INTRODUCTION
• Clinical trial is a systematic investigation in human subjects for evaluating the safety & efficacy of any new drug. • Clinical trials are a set of tests in medical research and drug development that generate safety and efficacy data for health interventions in human beings.
Clinical trials are conducted only when
- Satisfactory information has been gathered on the quality of the nonclinical safety
- Health authority/ethics committee approval is granted in the country where approval of the drug is sought.
- Clinical Trial is the mainstay for bringing out New Drugs to the Market.
DRUG REVIEW STEPS
1. Pre-clinical (animal) testing.
2. An investigational new drug application (IND) : outlines what the sponsor of a new drug proposes for human testing in clinical trials.
3. Phase 1 studies
4. Phase 2 studies
5. Phase 3 studies
6. Submission of New Drug Application (NDA) is the formal step asking the FDA to consider a drug for marketing approval.
7. FDA reviewers will approve the application or find it either “approvable” or “not approvable.“
8. Phase 4 studies
DRUG REVIEW
- Before one can initiate testing in human beings, extensive pre- clinical or laboratory research is required
- Research usually involves years of experiments in animal and human cells.
- If this stage of testing is successful, the sponsor then provides this data to the FDA requesting approval to begin testing in humans.This is called an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application
- If approved by the FDA, testing in humans begins. This is done through a formally written and approved protocol.
PRECLINICAL EVALUATION PHASE (ANIMAL STUDIES)
Major areas are:
- Pharmacodynamic studies in vivo in animals, In vitro preparation
- Absorption, distribution , elimination studies (pharmacokinetics)
- Acute ,sub acute, chronic toxicity studies (toxicity profile)
- Therapeutic index (safety & efficacy evaluation)
IND APPLICATION FILING
Once preclinical studies have indicated the safety and efficacy of a drug an IND application has to be filed with the regulatory authorities.
For obtaining regulatory Approval for Phase I, phase II and Phase III clinical evaluation.
Contents of IND application:
- Preclinical Data (All data from animal studies)
- Information on composition and source of drug • Chemical and manufacturing information • Proposed clinical plans and protocol
- Ethical Committee Clearance
PHASE 0 STUDY/MICRO DOSING
- Study of new drug in micro doseS to derive PK information in human before undertaking phase I studies is called PHASE O
- Micro dose: Less than 1/100 of the dose of a test substance calculated to produce pharmacological effect with a max dose ≤100 micrograms
- Objective: To obtain preliminary Pharmacokinetic data.
- Preclinical Data: Sub acute toxicity study in one species by two routes of administration.
PHASE 0 STUDY/MICRO DOSING
• Advantages:
Less chances of adverse effects
Short duration
Less no. of volunteers
Reduced cost of development
Reduced drug development time
• Limitations:
Study mainly based on PK parameters – not efficacy and safety based
Agents having different kinetic characteristics between micro dose and full dose are not evaluated by phase 0 trials Of Limited use for agents having Non linear PKs
The laboratory parameters are very limited and expensive, researchers have to depend on BA/BE labs
PHASE 1
• First stage of testing in human subjects.
• Designed to assess the safety, tolerability, PK and PD of drug.
• 20-25 healthy volunteers; Duration: 6-12 months.
• Patients: Anticancer drugs, AIDS therapy.
• The aim of a Phase I trial is to determine the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of the new treatment.
Kinds of Phase I:
- SAD: Single ascending dose studies.
- MAD: Multiple ascending dose studies.
- Food Effect: Investigates differences in absorption caused by food.
PHASE 1 SUBJECTS:
- Healthy human volunteers: Commonly used.
- Patient Volunteers: Cytotoxic drugs, AIDS therapy -Patients in advanced stage of disease.
LIMITATIONS:
- Trial restricted to homogenous subjects.
- Performance extrapolated to heterogeneous market place.
PHASE 2
• It is a Therapeutic Exploratory Trial consists of 20-300 Subjects.
• To confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, & further evaluate safety.
• First in patients (who have the disease that the drug is expected to treat).
• Duration: 6 months to several years.
Optimum dose finding:
- Dose efficacy relationship
- Therapeutic dose regimen
- Duration of therapy
- Frequency of administration
- Therapeutic window
• For New Actions of a marketed drug, start with Phase II (Phase I exemption obtained).
Phase II Study Types:
- Phase IIA: Designed to assess dosing requirements.
- Phases IIB: Designed to study efficacy.
PHASE 3
- It is a Therapeutic confirmatory trial.
- Target population: several 100’s to 3000 patients.
- Duration:Takes a long time, up to 5 years.
- To establish efficacy of the drug against existing therapy in larger number of patients, method of usage, & to collect safety data etc.
- To assess overall and relative therapeutic value of the new drug Efficacy, Safety and Special Properties
PHASE 3 :Subtypes:
- Phase IIIA: to get sufficient and significant data.
- Phase IIIB: allows patients to continue the treatment, Label expansion, additional safety data.
- Phase III B studies are known as “label expansion” to show the drug works for additional types of patients/diseases beyond the original use for which the drug was approved for marketing.
End Of Clinical Trial Activities
- Sponsor: Expert Committee review of Efficacy, safety and potential sales (Profit).
- Go-No Go decision to file new drug application with DCGI.
- Expert review by DCGI’s Committee
- DCGI approval.
- NCE marketed Phase IV begins
NDA: New Drug Application
NDA Refers to New Drug Application.
Formal proposal for the FDA/DCGI to approve a new drug for sale.
Sufficient evidences provided to FDA/DCGI to establish:
• Drug is safe and effective.
• Benefits outweigh the risks.
• Proposed labeling is appropriate.
NDA contains all of the information gathered during pre-clinical to phase III.
PHASE 4
Post Marketing Surveillance (PMS).
No fixed duration / patient population.
Helps to detect rare ADRs, Drug interactions and also to explore new uses for drugs [Sometimes called Phase V].
PERIODIC SAFETY UPDATE REPORTS :
To be submitted by the manufacturer every 6 months for 2 yrs and then annually for next 2 yrs after marketing approval.
Harmful effects discovered may result in a drug being no longer sold, or restricted to certain uses
OBJECTIVES OF PHASE 4:
Confirm the efficacy and safety profile in large populations during practice.
Detect the unknown/rare adverse drug reaction/s.
Evaluation of over-dosage. Identifications of new indications. Dose refinement: Evaluation of new formulations, dosages, durations of treatment.
REPORTING OF ADR:
The ADR can be reported to a formal reporting system such as: WHO International System USFDA- Medwatch UK- Yellow card system INDIA- National Pharmacovigilance Programme (CDSCO)
CONCLUSION
Clinical trial is a human experiment designed to study the efficacy and safety of a new drug/intervention.
Involves Phase 1-4 with specific objectives and end results.
Application to Regulatory authority:
• IND – Permission to conduct CT
• NDA – Permission to Market New drug.
Well designed and effectively executed clinical trials form the base of therapeutic decisions.
CT must follow guidelines & protocol to ensure well- being of participants.
Ultimate Goal of Drug Development
REFERENCE • Clinical trials.gov • Wikipedia • WWW.nlm.nih.gov/services/ctphases.html • WWW.cancerresearchuk.org • WWW.centrewatch.com > home > clinical trials Images : Google Images 26 PHASES OF CLINICAL TRIALS 25PHARMACEUTICAL BIOTECHNOLOGY