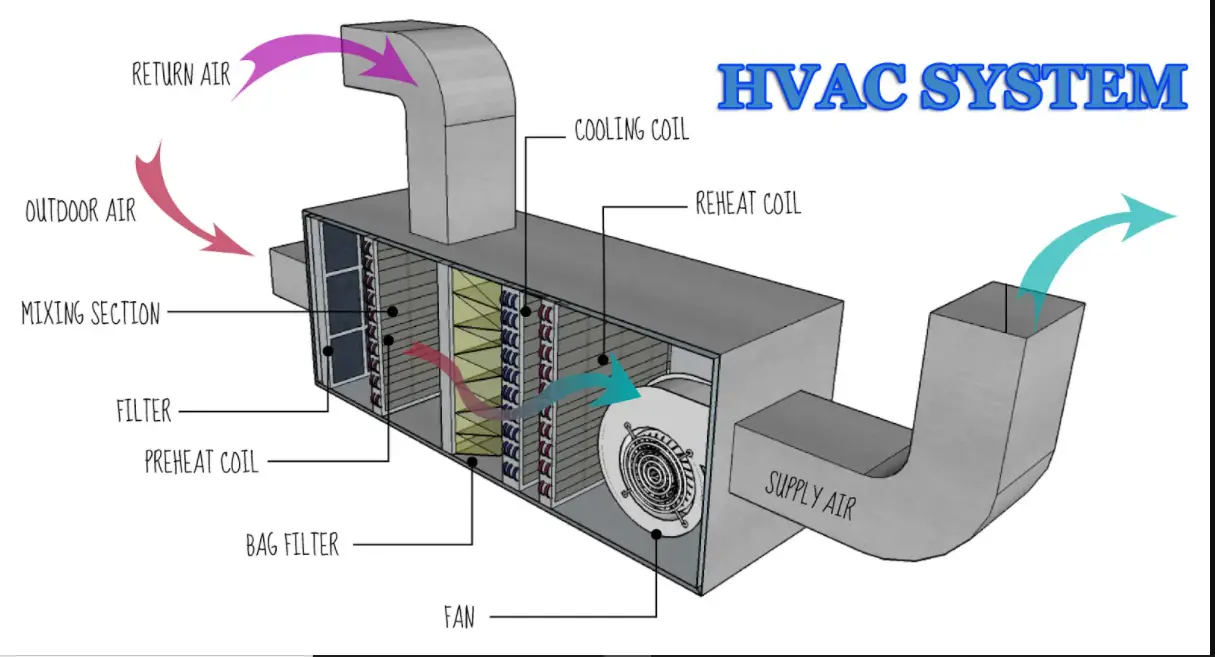
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING (HVAC) SYSTEMS:
- To avoid cross-contamination and to maintain relative humidity, temperature, and Pressure Difference of the manufacturing areas with Air handling Units,
- Air handling Units Provided in the manufacturing, warehouse, quality control, and microbiology section. Temperature and humidity are controlled and maintained within the limits as per the requirement of the product.
- The pre-filters are cleaned as per the frequency described in the SOP for cleaning the filters.
- In case of pressure differential failure, all the production activities are stopped and the filters are replaced with cleaned filters.
Validation of air handling unit is done through the studies of parameters like –
- Air velocity,
- Air change per hour,
- Temperature,
- Relative humidity,
- Non-viable particle count,
- HEPA filter integrity,
- The pressures differential across HEPA filter,
- Airflow visualization,
- Recovery test,
- Viable particle count, except recovery study similar studies, are done for RLAFs (Dispensing and sampling booths).
- In the processing area daily monitoring of differential pressure, temperature, and relative humidity.
- Microbial monitoring IS BEING DONE in the critical processing manufacturing area on daily basis and weekly for non-critical areas, and daily in the microbiological section.
- Critical manufacturing areas have a positive differential relative to adjacent less clean areas to avoid cross-contamination.
- The return air is passed through the return air riser and 90% of it is again re-circulated with the intake of 10% fresh air every cycle.
- The return air risers are located in critical process areas.
- Filters are arranged in the series of 10m (return air filter), 05 m (pre-filter), 03µ (fine filter) and 0.3m (HEPA filter) for critical areas, and for non-critical areas filters are put in the series of 10m 5m and 3µ arrangements.
Air changes are at least
- 20-60 Air changes per hour in ISO-8 (100,000) classified area,
- 60-80 Air changes per hour into-7 (10,000),
- 80 – 120 Air changes per hour in ISO-6 (1000 surrounding LAF) and
- 240-480 Air changes per hour in ISO-5(100 under LAF)